This is part of this series of posts: Oracle 12c on Oracle Linux 6
In this step we’ll configure a virtual machine that we will install Oracle Linux on in the next step.

Double click the Oracle VM VirtualBox icon on your desktop.

Click New to create a new VM.
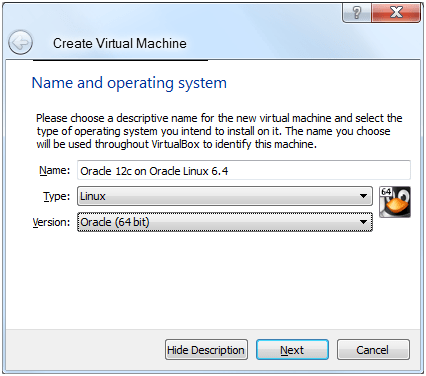
Enter Oracle 12c on Oracle Linux 6.4 as the name, choose Linux for the type and Oracle (64 bit) as the Version.
Note:
Make sure that the Version is Oracle (64 bit) and not just Oracle which ends up getting auto populated for you.
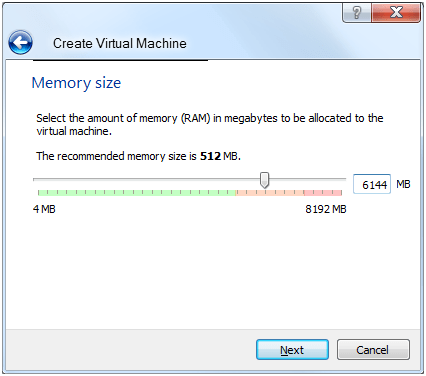
Enter an amount of memory and click Next.
Note:
Use as much memory as you can on your machine. Since I’ve got 8 GB of RAM, I used 6 GB for the virtual machine. If you use less than 4 GB of memory, you’ll get some warnings during the install of Oracle grid which you can ignore. If you only have 4 GB of RAM total on your machine, then use at least 3 GB for the VM.
If you only have 4 GB of RAM on your machine then it might be better to go with 11g R2 instead of 12c. Some folks have had failures when only 4GB was allocated to the virtual machine.

Choose Create a virtual hard drive now and click Create.

Select VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) and click Next.

Choose Dynamically allocated and click Next.
Note:
This is a test system so we’re going to go with dynamically allocated disks. Fixed size disks are faster, but they will take up much more room. Using all the disk sizes presented in the guide, I ended up with 40.5 GB of used space for the VM by the end of the install.

Change the size to 100 GB and click Create.
Note:
When entering the size in the box (much easier than using the slider) you have to add the GB at the end of your 100 to get 100 GB. If you don’t put the GB you’ll end up with 100 MB which won’t work.

Click the word System in the details pane to bring up the System dialog box.

Remove the Floppy (uncheck) and optionally change the order of the Hard Disk and the CD/DVD-ROM.

Click the Processor Tab and enter the number of processors.
Note:
Ideally you can set this to be as many physical cores as there are on your CPU(s), I chose 4.

Click the Acceleration tab and confirm that the two boxes are checked.
Note:
Remember that your processor has to support these features.

Select the Storage choice on the left hand side of the dialog and then select Empty below the Controller: IDE and then click the disk icon in the Attributes section.

Navigate to your Downloads folder, select the Oracle Linux 6.4.iso file and click Open.

You should see the Oracle Linux 6.4.iso under the Controller: IDE.

Select Controller: SATA in the Storage Tree and click on the Add Hard Disk icon (the one on the right).

Click Create new disk.

Choose VDI (Virtual Disk Image) and click Next.

Choose Dynamically allocated and click Next.

Name the disk ASMDISK01 and change the size to 300 GB.
Note:
300GB is big, but using Oracle 12c Oracle now requires 22 GB to install a container DB with a pluggable DB. 300 GB is also a common size for fast 15K hard drives, so I went with 300 GB. Since these are dynamically allocated disks, they are not going to take up 300 GB each. If you decided to go the fixed disk route, then you’ll need to make these about 12 GB each.

Repeat the previous ASM disk creation steps 12 more times changing the disk names to ASMDISK02 to ASMDISK13.
Note:
We really only need this many disks to follow the Oracle training (for 11g classes). 8 gives us 4 each for the +DATA and +FRA disk groups which would be more than enough.

When finished you should have a storage configuration that looks like the above. Click OK.
Oracle Database 12c on Oracle Linux 6 – Step 2: Download the Oracle Linux 6.4 iso < Previous Post – Next Post > Oracle Database 12c on Oracle Linux 6 – Step 4: Install Oracle Linux in the Virtual Machine










































































































